The treatment regimen of autologous endometrial stem cells and sodium hyaluronate gel combined with estrogen and aspirin has significantly improved pregnancy and live birth rates in patients with moderate to severe uterine adhesions, bringing hope for fertility to women who have suffered from long-term uterine adhesions.
On May 1, a clinical study jointly conducted by Xiangya Tri-Institutes and Xiangtan Central Hospital made important progress, and the article was published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy.
The research team significantly improved endometrial repair and pregnancy outcomes in patients with recurrent moderate-to-severe intrauterine adhesions (IUA) through intrauterine infusion of autologous endometrial stem cells combined with sodium hyaluronate gel infusion and hormonal supportive therapy. A follow-up period of 2 years was achieved with 100% effectiveness and up to 60% overall pregnancy rate.
Research highlights
In response to the clinical problems of high recurrence rate and low pregnancy rate after traditional hysterosalpingolysis (HA), the research team innovatively adopted autologous endometrial stem cells as the core of regenerative medicine treatment.
The stem cells are derived from the patient’s own endometrial tissue, which are obtained through hysteroscopy, collagenase digestion, gradient centrifugation, and in vitro expansion culture to obtain high-purity mesenchymal stem cells (CD29/CD44/CD90 positivity rate >95%).
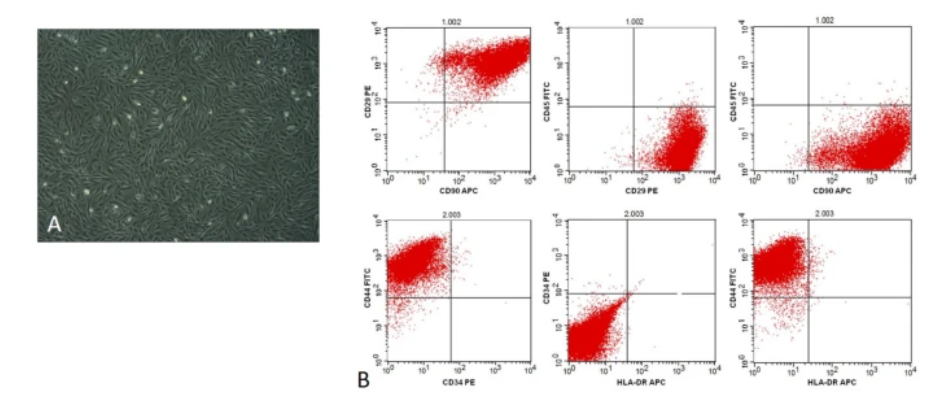
Characterization of endometrial stem cells. (A) Microscopic morphology of endometrial stem cells. (B) Phenotyping of second-generation endometrial stem cells by flow cytometry
The team further optimized the concentration of sodium hyaluronate gel to 12.5%, confirming that it did not inhibit stem cell activity and effectively prolonged the residence time of stem cells in the uterine cavity.
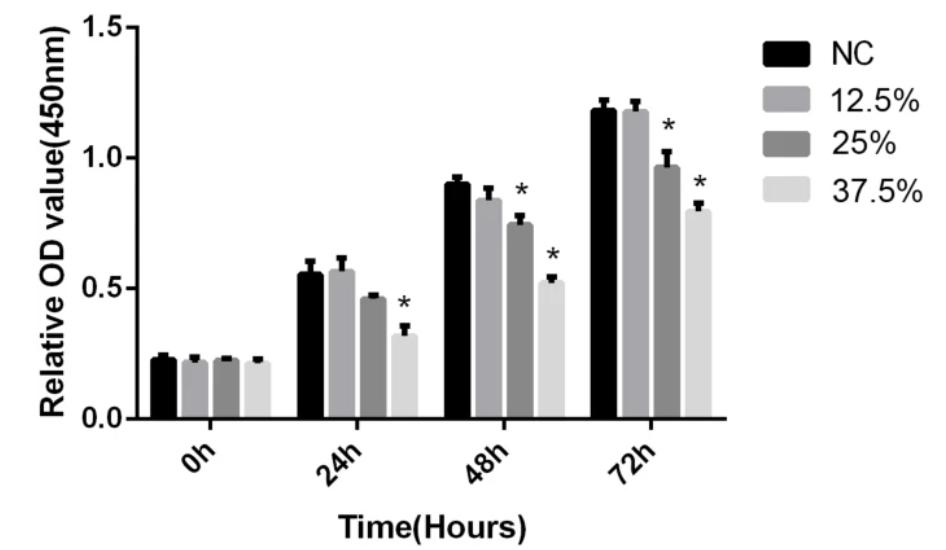
Endometrial stem cell value added by different concentrations of sodium hyaluronate gel (*P<0.05)
Treatment Strategies
Fifteen patients with recurrent moderate-to-severe IUA (AFS score ≥6) were included in the study, and the treatment regimen consisted of:
1.stem cell infusion
Intrauterine infusion of 1×10^7 fifth-generation autologous endometrial stem cells combined with 12.5% sodium hyaluronate gel on day 1 of the menstrual cycle;
2.Auxiliary support
Postoperative oral estradiol valerate (3 mg/day) and acetylsalicylic acid (50 mg/day) were administered to promote endometrial angiogenesis and improved blood flow;
3. Dynamic monitoring
Endometrial thickness and degree of adhesions were assessed by hysteroscopy and ultrasound every 2-3 months, and a second round of stem cell therapy was performed if necessary.
Clinical results
The degree of uterine adhesions significantly improved in all patients after treatment (decrease in AFS score, 100% efficiency), and endometrial thickness returned to transplantable levels (≥6 mm) in 8 of them.
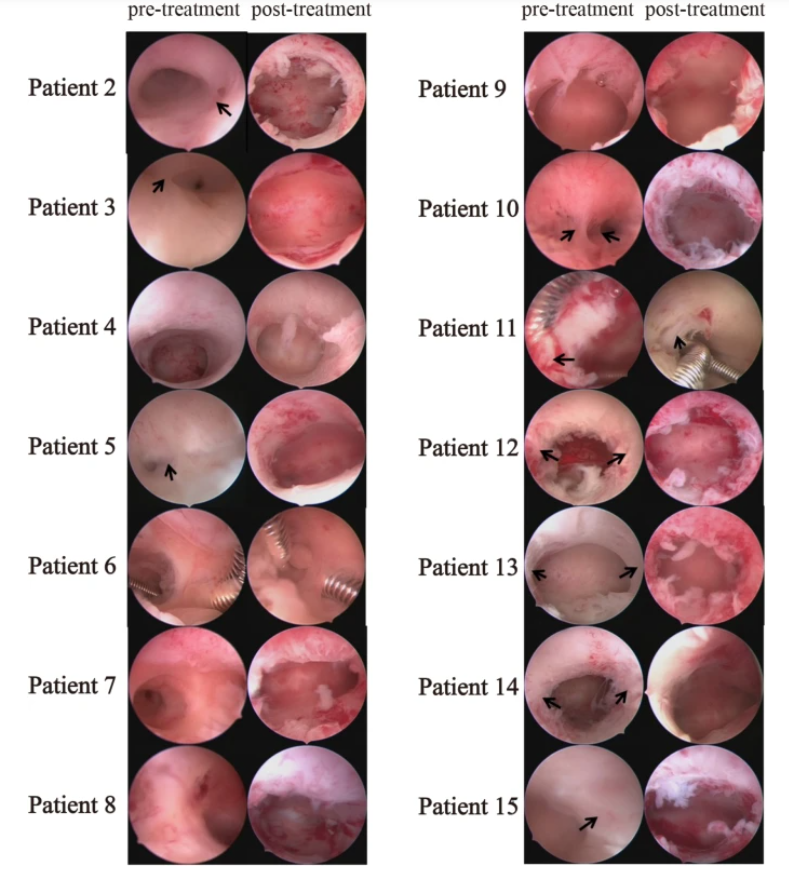
Hysteroscopic images of IUA patients before and after endometrial stem cell therapy
Within 2 years of follow-up, the overall pregnancy rate reached 60% (9/15), the live birth rate was 53.3% (8/15), and one spontaneous abortion (endometrial thickness of less than 6 mm) was reported, with no treatment-related adverse effects.
The study data suggest that this combination therapy is superior to single interventions such as traditional IUDs or balloon catheters in terms of key indicators such as pregnancy rate and live birth rate.
Significance of the research
Expert comment, “Autologous stem cell therapy avoids the risk of immune rejection, and endometrial-derived stem cells have tissue-specific repair advantages. Combined with sodium hyaluronate gel and hormonal support, it forms a multi-dimensional treatment system of ‘repairing-anti-adhesion-promoting growth’.”
This achievement provides a new regenerative medicine solution for patients with severe uterine adhesions, and the long-term safety will be further validated by expanding the sample size and multicenter studies in the future.
Disclaimer: The information in this article comes from the Internet, this article is only for the purpose of knowledge exchange and sharing and popularization of science, does not involve commercial propaganda, and does not serve as relevant medical guidance or medication advice. Please contact us for deletion if there is any infringement. Source: Cellplus


